
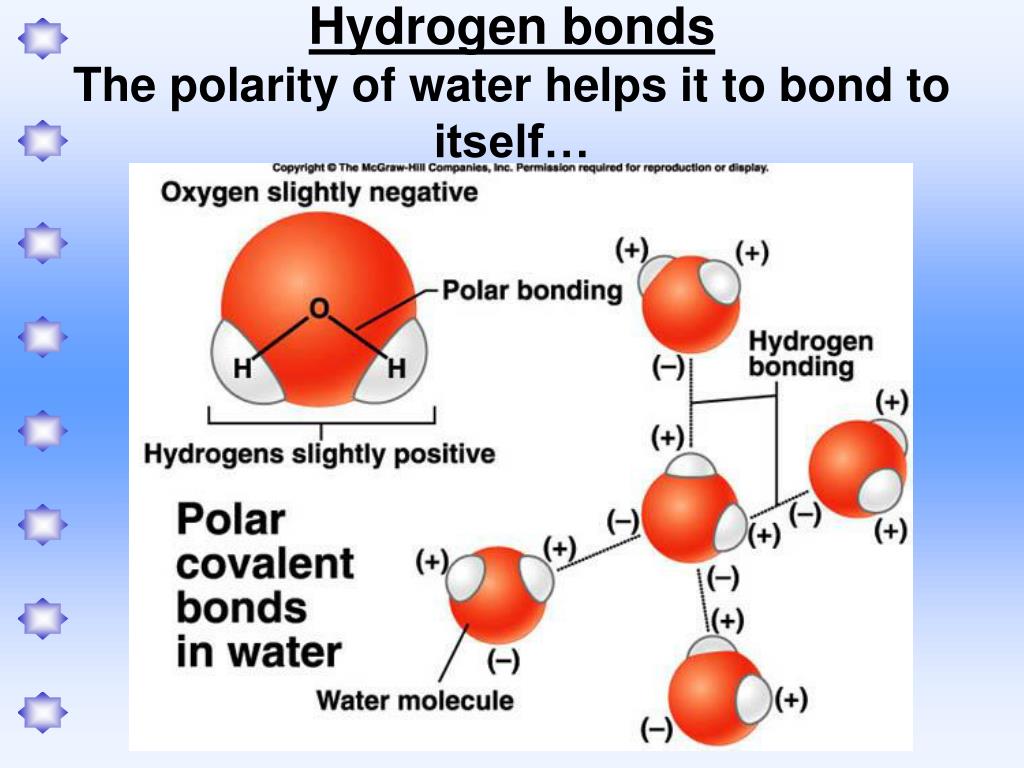
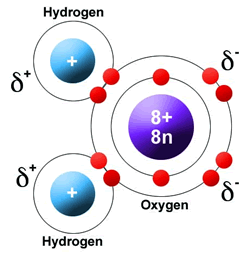
It also allows water to move through plant roots and stems, thermometers, and the smallest blood vessels in your body. Surface tension causes water to clump in drops rather than spreading out in a thin layer. Insects that walk on water are taking advantage of this surface tension. The molecules at the surface of the water “stick together” to form a type of ‘skin’ on the water, strong enough to support very light objects. Wherever water goes, it carries dissolved chemicals, minerals, and nutrients that are used to support living things.īecause of their polarity, water molecules are strongly attracted to one another, which gives water a high surface tension. Water dissolves more substances than any other liquid – even the strongest acid! Because of this, it is often called the ‘universal solvent.’ The dissolving power of water is very important for life on Earth. The attractions cause the molecules of the new substance to be mixed uniformly with the water molecules. When a polar substance is put in water, the positive ends of its molecules are attracted to the negative ends of the water molecules, and vice versa. What does this mean for us? Water’s polarity allows it to dissolve other polar substances very easily. Just like in a magnet, where north poles are attracted to south poles (‘opposites attract’), the positive end of the water molecule will connect with the negative end of other molecules. The other end, with the oxygen, is negatively charged. The end of the molecule with the two hydrogen atoms is positively charged. This molecular structure gives the water molecule polarity, or a lopsided electrical charge that attracts other atoms. When the two hydrogen atoms bond with the oxygen, they attach to the top of the molecule rather like Mickey Mouse ears. The Dissolved Oxygen Handbook: A Practical Guide to Dissolved Oxygen Measurements. Winkler’s method overestimates dissolved oxygen in seawater: iodate interference and its oceanographic implications. Berichte der Deutschen chemischen gesellschaft, 21, 2843–2855.
Die bestimmung des in wasser gelösten sauerstoffen. Measurement and interpretation of low levels of dissolved oxygen in ground water. The solubility of nitrogen, oxygen and argon in water and seawater. Change to solubility equations for oxygen in water: Office of Water Quality Technical Memorandum 2011.03. Water quality – new tables of dissolved oxygen saturation values: Quality of Water Branch Technical Memorandum 81.11. UNESCO Technical Papers in Marine Science, 38, 192. Background papers and supporting data on the International Equation of State of Seawater 1980. available from the International Argo Program. Processing Argo OXYGEN data at the DAC level. Thierry, V., Gilbert, D., Kobayashi, T., and Schmid, C., 2013. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Bulletin, 167, pp.

In A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis. Luminescence Based Measurement of Dissolved Oxygen in Natural Waters. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, book 9, chap. Oxygen solubility in sea water: better fitting equations. Limnology and Oceanography, 10, 141–143.Įutech Instruments Pte Ltd., 1997. The Chesapeake Bay Institute technique for the Winkler dissolved oxygen method. Limnology and Oceanography, 14, 450–454.Ĭarpenter, J. Colorimetric determination of dissolved oxygen at low concentration. Limnology and Oceanography, 29, 620–632.īroenkow, W. The concentration and isotopic fractionation of oxygen dissolved in freshwater and seawater in equilibrium with the atmosphere. Limnology and Oceanography, 25, 662–671.īenson, B. The concentration and isotopic fractionation of gases dissolved in freshwater in equilibrium with the atmosphere. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation, pp. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn. APHA American Public Health Association, 2005.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
